题目内容
US scientists say they have developed the technology to ________ painful memories without hurting a person’s brain and hope it can help those sufferers.
A. leave B. remove C. ignore D. separate
B

 全能测控期末小状元系列答案
全能测控期末小状元系列答案Futurologists predict that life will probably be very different in 2050.
TV channels will have disappeared. Instead, people will choose a program from a “menu” and a computer will send the program directly to the television. Today, we can use the World Wide Web to read newspaper stories and see pictures on a computer thousands of kilometers away. By 2050, music, films, programs, newspapers, and books will come to us by computer.
Cars will run on new, clean fuels and they will go very fast. Cars will have computers to control the speed and there won’t be any accidents. Today, many cars have computers that tell drivers exactly where they are. By 2050, the computer will control the car and drive it to your destination. Space planes will take people halfway around the world in 2 hours. Today, the United States Space Shuttle can go into space and land on Earth again. By 2050, space planes will fly all over the world and people will fly from Los Angeles to Tokyo in just 2 hours.
Robots will have replaced people in factories. Many factories already use robots. Big companies prefer robots — they don’t ask for pay rises or go on strike, and they work 24 hours a day. By 2050, we will see robots everywhere — in factories, schools, offices, hospitals, shops and homes.
Medical technology will have conquered many diseases. Today, there are devices(设备)that connect directly to the brain to help people hear. By 2050, we will be able to help blind and deaf people to see and hear again.
Scientist will have discovered how to control genes(基因). Scientists have already produced clones of animals. By 2050, scientists will be able to produce clones of people, and decide how they look, how they behave and how clever they are. Scientists will be able to do these things, but should they?
【小题1】We can learn from the passage that some big companies prefer robots to human workers, because human workers __________.
| A.often ask for more pay |
| B.can work 24 hours a day |
| C.are not clever enough |
| D.are often late for work |
| A.discovered | B.treated | C.caused | D.cured |
| A.few diseases will attack people by 2050 |
| B.there will be no blind and deaf people by 2050 |
| C.medical technology will be more effective by 2050 |
| D.devices are connected directly to the brain to help people hear |
| A.The author does not support the use of cloning technology. |
| B.The author thinks human cloning is impossible. |
| C.The author does not really support the idea of human cloning. |
| D.The author is quite excited about human cloning. |
| A.Read newspapers on a computer. |
| B.Make a space shuttle to go into the land. |
| C.Use computers to control car speed. |
| D.Choose TV programs freely from a “menu”. |
Scientists have proved that sleeping and learning go hand in hand. Even a short nap can boost our memory and sharpen our thinking. But the relationship goes deeper than that.
“The brain is not passive while you sleep,” scientist Anat Arzi said. “It’s quite active. You can do many things while you are asleep.”
Arzi and her coworkers didn’t try to teach the sleeping volunteers any complex information, like new words or facts. Instead, the scientists taught volunteers to make new connections between smells and sounds.
When we smell something good, like a flower, we take deep breaths. When we smell something bad, we take short breaths. Arzi and her co-workers based their experiment on these reactions.
Once the volunteers fell asleep in the lab, the scientists went to work. They gave them a whiff of something pleasant and meanwhile played a particular musical note. They didn’t wake up, but they heard—and sniffed(吸气) deeply. Then the scientists gave the volunteers a whiff of something terrible and played a different musical note. Again, the volunteers heard and smelled—a short snort this
time—but didn’t wake up. The researchers repeated the experiment.
After just four repetitions, volunteers made a connection between the musical notes and their paired smells. When the scientists played the musical tone that went with good smells, the sleepers breathed deeply. And when the scientists played the musical tone that went with bad smells, the sleepers breathed briefly—despite there being no bad smell.
The next day, the volunteers woke up with the sound-smell connection. They breathed deeply when hearing one tone and cut their breaths short when hearing the other, which must have been unusual for them. Imagine walking down the street and taking a deep breath upon hearing a particular sound!
【小题1】In the study, the volunteers were taught _______.
| A.to become active during sleep |
| B.to tell the difference between smell |
| C.to learn new words and scientific facts |
| D.to make sound-smell connections |
| A.They took a deep breath. | B.They had a wonderful dream. |
| C.They woke up at once. | D.They took a short breath. |
| A.learned how to play to musical tones |
| B.forgot what happened during their sleep |
| C.continued with the sound-smell connection |
| D.changed their reaction when hearing. |
| A.special smells and sounds can improve our memory. |
| B.our brain can actually learn something new during the sleep. |
| C.the volunteers will always hear similar sounds in the street. |
| D.our brain can tell the difference between smells during the sleep. |
| A.A short sleep can improve our memory and sharpen our thinking. |
| B.Arzi and her coworkers didn’t try to teach the sleeping volunteer some simple information. |
| C.When the volunteer smelt something terrible, they didn’t wake up. |
| D.After four repetitions, volunteers made a connection between the musical notes and their pared smells. |
| 任务型阅读。 | |
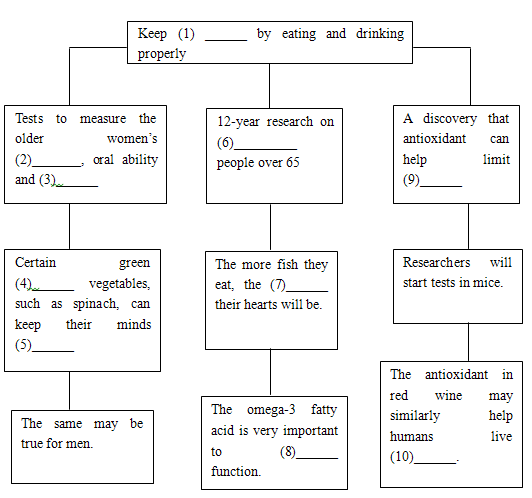
| Vegetables may aid the brain A study suggests certain vegetables such as broccoli(西兰花)and spinach(菠菜)might help older women keep their minds sharp. Researchers have discovered that women in their 60s who eat more green leafy vegetables how less signs of mental decline over time, reported Wednesday's CRI online. They gave participants a bundle of tests measuring memory, oral ability and attention. The study didn't include men, but researchers say a similar diet would likely have the same results. Eating fish can cut risk of heart rhythm disorder US scientists have found that eating fish can reduce the risk of deadly heartbeat disorders. They say baked fish can effectively reduce the risk of atria fibrillation(心房颤动)among older men and women, reported Tuesday's CRI online. Researchers say in their 12 years of research among 4,800 people over the age of 65, they found those who ate fish one to four times per week had an about 30 percent lower risk compared with those who ate fish less than once a month. They say the omega-3 fatty acid can reduce the risk of a range of heart disorders and is vital to brain development and function. Red wine may extend life US scientist have found that a mixture that makes red wine a healthy drink may also hold the secret to a longer life. They say antioxidant(抗氧化剂) in wine acted on fruited flies and worms in the same way as a method known to extend the life of many animals, which is by sharply limiting how much they eat. Limiting calories has been shown to make animals such as dogs and monkeys live longer, but they are often tired and lose productivity. The researchers will begin testing the mixture in mice. | |
 |