网址:http://m.1010jiajiao.com/timu3_id_3035126[举报]
Beijing's historic hutong are in danger of disappearing. That's the warning from residents and historians, who have called on authorities to do more to protect this unique part of the capital's culture.
In 2000, Beijing still had 1,300 hutong, according to amateur historian Zhang Wei. But he estimates that since then, at least half of them have disappeared.
According to regulations, people can report illegal buildings to urban patrol officers, known as chengguan, and buildings found to be illegal will be demolished by force.
However, a China Daily reporter found that it was not an easy task, and lots of additional structures built by their owners were found in hutong. Many owners added a second floor or even more floors to their houses, especially in buildings near main streets, in order to rent more apartments and make more money.
Zhang, the historian, said that to better protect the hutong, the government should offer more compensation to residents willing to move away. Guo Dazhi, a photojournalist in Beijing, lived in a hutong for nearly 30 years before moving to eastern Chaoyang district. Guo hopes that the government can solve the problem by moving residents out of hutong with policies such as public renting programs.
However, the Beijing Commission of Urban Planning said in a report in July that the relocation of residents from old areas was very expensive.According to the report, allocating 10,000 residents costs 1.5 billion yuan .
66. What made Beijing’s historic hutong in danger?
A. The fast development of the city B. Some people build unlawful construction
C. Population growing D. Pollution
67. What does demolish mean in para.3?
A .pull down B. build up C. clean up D. wash up
68. Who is mainly in charge of the illegal building?
A .Policemen B. The army C. Chengguan D. The local committee
69. What is the suggestion mentioned of solving the problem?
A. moving residents out of hutong with force B. introduce social capital for investment in constructure
C. offer more money to residents willing to move away. D. build more hutong
70. How many hutong exist up till now?
A. 1300 B.300 C. 2000 D.600
查看习题详情和答案>>London has always been known for its "black fogs. “ In the winter of 1952,a milky white fog rolled into the city. As the smoke poured into the air, it was so hard to see that people had to walk in front of the buses to guide them. In this way, the most serious air pollution disaster in history began. When it was over, more than 4,000 people had been killed by the thick black smog.
New York City has had several London-type smogs since 1950. Each time, there were from 100 to 400 deaths caused by the smog. Although these smogs were not as deadly as London’ s,
New York City has the worst air pollution problem in the United States.
In all the killer smogs, factories and homes poured smoke and fumes into the air from the furnaces. The chemical fumes combined with the water droplets in the fog to form harmful substances. These substances caused the illness of those who breathed the polluted air.
Usually, such harmful fumes rise into the upper air and are blown away by the wind. But sometimes there is an unusual weather condition called a temperature inversion. A layer of cold air remains near the ground as smoke and fumes pour into it. This is covered by an upper layer of warm air that acts like a lid. It prevents the polluted cooler air from rising. The harmful fumes pile up and make people ill. The smog may be so thick that airports are closed and chains of collisions occur on the highways.
Another type of smog occurs in Los Angeles. Here the weather may be clear and sunny. But stinging eyes and dry coughs show that harmful chemicals fill the air. The smog is due to invisible gases, mostly from automobile exhaust. Because these chemicals are changed by the sun high up in the air, it is called photochemical smog. It contains automobile exhaust fumes and nitrogen oxides changed by the sun's rays. Added to these are sulfur dioxide and other fumes from factories and oil refineries. Photochemical smog is found in many large cities all over the world.
Killer smogs don,t happen very often, fortunately. But in Beijing, a combination of automobile exhaust fumes, home furnace smoke, and factory waste gases pours into the air. This may also happen in the suburbs, or out in the country, where large factories have been built. A number of harmful substances have been found in the air there. When these substances are breathed in day after day ,the health of the population is affected.
51. Why do people call this phenomenon " black fog" ?
A. It is black and dirty. B. It can affect the health.
C. It can kill people. D. It is too thick for people to see something.
52. What can reduce the air pollution according to the passage?
A. Water. B. Wind. C. The sun. D. Cold air.
53.When photochemical smog happens in the city, _____.
A. many people will be killed B. black smoke may pour into the air
C. the weather may be fine D. people have to walk to work
54.From the passage we know that the most serious black smog disaster took place in_____
A, London B. New York C. Los Angeles D. Beijing
查看习题详情和答案>>
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1995 ten of the largest cities in the world have a total population of 152.5 million. How does it spread out ? How does it distribute? Let's have a look at the circle below. We divide the ten cities into five groups : Group A : Tokyo in Japan and Seoul in Korea. Group B: Sao Paulo in Brazil and Mexico City in Mexico. Group C: New York and Los Angeles in the U.S.A. Group D: Bombay and Calcutta in India. Group E: Shanghai and Beijing in China. If l52.5 million is supposed to be 100% in 360° circle, then each group’s population takes a certain percent of the 152.5 million in total, a certain part of the circle, a certain number of degrees in a central angle in the 360 ° circle.
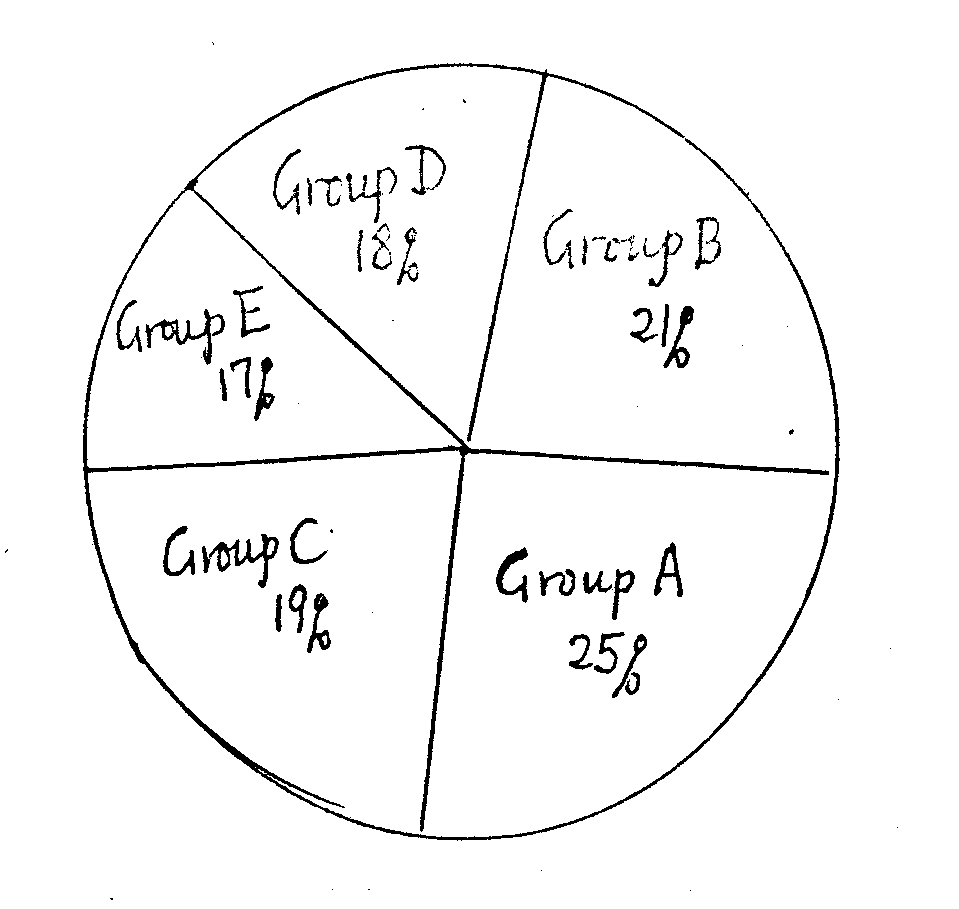
1.What was the total population in Shanghai and Beijing in 1995?
A.24. 7 million. B. 25.7 million. C. 26.7 million. D. 27.7 million
2.What was the total population in Sao Paulo and Mexico City in 1995?
A.31 million. B. 32 million. C. 33 million. D. 34 million.
3.How many more million of people were there in Group A than in Group C?
A.6.15 million. B. 7.25 million. C. 8.15 million. D. 9.15 million.
4.How many degrees are there in the central angle of the part for the total population of Bombay and Calcutta?
A.64.8° .B. 74.8° . C. 44.8° . D. 54.8° .
5.What is the ratio (比例) of the total population of New York and Los Angeles to the total population of Tokyo and Seoul?
A.1/5 B.2/5 C.3/5 D. 4/5
查看习题详情和答案>>