网址:http://m.1010jiajiao.com/timu3_id_2482250[举报]
Sustainable development is applied to just about everything from energy to clean water and economic growth, and as a result it has become difficult to question either the basic assumptions behind it or the way the concept is put to use. This is especially true in agriculture, where sustainable development is often taken as the only measure of progress without a proper appreciation of historical and cultural perspectives.
To start with, it is important to remember that the nature of agriculture has changed markedly throughout history, and will continue to do so. Medieval agriculture in northern Europe fed, clothed and sheltered a popularly rural society with a much lower population density than it is today. It had smallest effect on biodiversity, and any pollution it caused was typically localized. In terms of energy use and the nutrients captured in the product it was relatively inefficient.
Contrast this with farming since the start of the industrial revolution. Competition from overseas led farmers to specialize and increase yields. Throughout this period food became cheaper, safer and more reliable. However, these changes have also led to habitat loss and to decreasing biodiversity.
What’s more, demand for animal products in developing countries is growing so fast that meeting it will require an extra 300 million tons of grain a year by 2050.yet the growth of cities and industry is reducing the amount of water available for agriculture in many regions.
All this means that agriculture in the 21st century will have to be very different from how it was in the 20th. This will require complete thinking. For example, we need to move away from the idea that traditional practices are unavoidably more sustainable than new ones. We also need to abandon the idea that agriculture can be “zero impact”. The key will be to abandon the rather simple and unchangeable measures of sustainability, which centre on the need to maintain production without increasing damage.
Instead we need a more dynamic explanation, one that looks at the pros and cons of all the various way land is used. There are many different ways to measure agricultural performance besides food yield: energy use, environmental costs, water purity, carbon footprint and biodiversity. It is clear, for example, that the carbon of transporting tomatoes from Spain to the UK is less than that of producing them in the UK with additional heating and lighting. But we do not know whether lower carbon footprints will always be better for biodiversity.
What is critical is recognizing that sustainable agriculture is not just about sustainable food production.
1.How do people often measure progress in agriculture?
A.By its productivity.
B.By its impact on the environment.
C.By its sustainability.
D.By its contribution to economic growth.
2.What does the author think of traditional farming practices?
A.They have remained the same over the centuries.
B.They have not kept pace with population growth.
C.They are not necessarily sustainable.
D.They are environmentally friendly.
3.What will agriculture be like in the 21st century?
A.It will go through thorough changes.
B.It will supply more animal products.
C.It will abandon traditional farming practices.
D.It will cause zero damage to the environment.
4.What is the author’s purpose in writing this passage?
A.To remind people of the need of sustainable development.
B.To suggest ways of ensuring sustainable food production.
C.To advance new criteria for measuring farming progress.
D.To urge people to rethink what sustainable agriculture is.
查看习题详情和答案>>
Sustainable development is applied to just about everything from energy to clean water and economic growth, and as a result it has become difficult to question either the basic assumptions behind it or the way the concept is put to use.This is especially true in agriculture, where sustainable development is often taken as the sole measure of progress without a proper appreciation of historical and cultural perspectives.
To start with, it is important to remember that the nature of agriculture has changed markedly throughout history, and will continue to do so .Medieval agriculture in northern Europe fed, clothed and sheltered a predominantly rural society with a much lower population density than it is today.It had minimal effect on biodiversity, and any pollution it brought about was typically localized.In terms of energy use and the nutrients captured in the product it was relatively inefficient.
Contrast this with farming since the start of the industrial revolution.Competition from overseas led farmers to specialize and increase yields.Throughout this period food became cheaper, safe and more reliable.However, these changes have also led to habitat loss and to diminishing biodiversity.
What’s more, demand for animal products in developing countries is growing so fast that meeting it will require an extra 300 million tons of grain a year by 2050,yet the growth of cities and industry is reducing the amount of water available for agriculture in many regions.
All this means that agriculture in the 21st century will have to be very different from how it was in the 20th.This will require radical(激进的)thinking.For example, we need to move away from the idea that traditional practices are inevitably more sustainable than new ones.We also need to abandon the notion that agriculture can be “zero impact”.The key will be to abandon the rather simple and static measures of sustainability, which centre on the need to maintain production without increasing damage.Instead we need a more dynamic interpretation, one that looks at the pros and cons of all the various way land is used.There are many different ways to measure agricultural performance besides food yield: energy use, environmental costs, water purity, carbon footprint and biodiversity.It is clear, for example, that the carbon of transporting tomatoes from Spain to the UK is less than that of producing them in the UK with additional heating and lighting, but we do not know whether lower carbon footprints will always be better for biodiversity.
What is crucial is recognizing that sustainable agriculture is not just about sustainable food production.
72.How do people often measure progress in agriculture?
A.By its productivity B. By its impact on the environment
C.By its sustainability D.By its contribution to economic growth
73.What does the author think of traditional farming practices?
A.They have remained the same over the centuries
B.They have not kept pace with population growth
C.They are not necessarily sustainable
D.They are environmentally friendly
74.What will agriculture be like in the 21st century?
A.It will go through radical changes
B.It will supply more animal products
C.It will abandon traditional farming practices
D.It will cause zero damage to the environment
75.What is the author’s purpose in writing this passage?
A.To remind people of the need of sustainable development
B.To suggest ways of ensuring sustainable food production
C.To advance new criteria for measuring farming progress
D.To urge people to rethink what sustainable agriculture is.
查看习题详情和答案>>
Sustainable development is applied to just about everything from energy to clean water and economic growth, and as a result it has become difficult to question either the basic assumptions behind it or the way the concept is put to use.This is especially true in agriculture, where sustainable development is often taken as the sole measure of progress without a proper appreciation of historical and cultural perspectives.
To start with, it is important to remember that the nature of agriculture has changed markedly throughout history, and will continue to do so .Medieval agriculture in northern Europe fed, clothed and sheltered a predominantly rural society with a much lower population density than it is today.It had minimal effect on biodiversity, and any pollution it brought about was typically localized.In terms of energy use and the nutrients captured in the product it was relatively inefficient.
Contrast this with farming since the start of the industrial revolution.Competition from overseas led farmers to specialize and increase yields.Throughout this period food became cheaper, safe and more reliable.However, these changes have also led to habitat loss and to diminishing biodiversity.
What’s more, demand for animal products in developing countries is growing so fast that meeting it will require an extra 300 million tons of grain a year by 2050,yet the growth of cities and industry is reducing the amount of water available for agriculture in many regions.
All this means that agriculture in the 21st century will have to be very different from how it was in the 20th.This will require radical(激进的)thinking.For example, we need to move away from the idea that traditional practices are inevitably more sustainable than new ones.We also need to abandon the notion that agriculture can be “zero impact”.The key will be to abandon the rather simple and static measures of sustainability, which centre on the need to maintain production without increasing damage.Instead we need a more dynamic interpretation, one that looks at the pros and cons of all the various way land is used.There are many different ways to measure agricultural performance besides food yield: energy use, environmental costs, water purity, carbon footprint and biodiversity.It is clear, for example, that the carbon of transporting tomatoes from Spain to the UK is less than that of producing them in the UK with additional heating and lighting, but we do not know whether lower carbon footprints will always be better for biodiversity.
What is crucial is recognizing that sustainable agriculture is not just about sustainable food production.
72.How do people often measure progress in agriculture?
A.By its productivity B. By its impact on the environment
C.By its sustainability D.By its contribution to economic growth
73.What does the author think of traditional farming practices?
A.They have remained the same over the centuries
B.They have not kept pace with population growth
C.They are not necessarily sustainable
D.They are environmentally friendly
74.What will agriculture be like in the 21st century?
A.It will go through radical changes
B.It will supply more animal products
C.It will abandon traditional farming practices
D.It will cause zero damage to the environment
75.What is the author’s purpose in writing this passage?
A.To remind people of the need of sustainable development
B.To suggest ways of ensuring sustainable food production
C.To advance new criteria for measuring farming progress
D.To urge people to rethink what sustainable agriculture is.
Sustainable development is applied to just about everything from energy to clean water and economic growth, and as a result it has become difficult to question either the basic assumptions behind it or the way the concept is put to use. This is especially true in agriculture, where sustainable development is often taken as the only measure of progress without a proper appreciation of historical and cultural perspectives.
To start with, it is important to remember that the nature of agriculture has changed markedly throughout history, and will continue to do so. Medieval agriculture in northern Europe fed, clothed and sheltered a popularly rural society with a much lower population density than it is today. It had smallest effect on biodiversity, and any pollution it caused was typically localized. In terms of energy use and the nutrients captured in the product it was relatively inefficient.
Contrast this with farming since the start of the industrial revolution. Competition from overseas led farmers to specialize and increase yields. Throughout this period food became cheaper, safer and more reliable. However, these changes have also led to habitat loss and to decreasing biodiversity.
What’s more, demand for animal products in developing countries is growing so fast that meeting it will require an extra 300 million tons of grain a year by 2050.yet the growth of cities and industry is reducing the amount of water available for agriculture in many regions.
All this means that agriculture in the 21st century will have to be very different from how it was in the 20th. This will require complete thinking. For example, we need to move away from the idea that traditional practices are unavoidably more sustainable than new ones. We also need to abandon the idea that agriculture can be “zero impact”. The key will be to abandon the rather simple and unchangeable measures of sustainability, which centre on the need to maintain production without increasing damage.
Instead we need a more dynamic explanation, one that looks at the pros and cons of all the various way land is used. There are many different ways to measure agricultural performance besides food yield: energy use, environmental costs, water purity, carbon footprint and biodiversity. It is clear, for example, that the carbon of transporting tomatoes from Spain to the UK is less than that of producing them in the UK with additional heating and lighting. But we do not know whether lower carbon footprints will always be better for biodiversity.
What is critical is recognizing that sustainable agriculture is not just about sustainable food production.
How do people often measure progress in agriculture?
A.By its productivity.
B.By its impact on the environment.
C.By its sustainability.
D.By its contribution to economic growth.
What does the author think of traditional farming practices?
A.They have remained the same over the centuries.
B.They have not kept pace with population growth.
C.They are not necessarily sustainable.
D.They are environmentally friendly.
What will agriculture be like in the 21st century?
A.It will go through thorough changes.
B.It will supply more animal products.
C.It will abandon traditional farming practices.
D.It will cause zero damage to the environment.
What is the author’s purpose in writing this passage?
A.To remind people of the need of sustainable development.
B.To suggest ways of ensuring sustainable food production.
C.To advance new criteria for measuring farming progress.
D.To urge people to rethink what sustainable agriculture is.
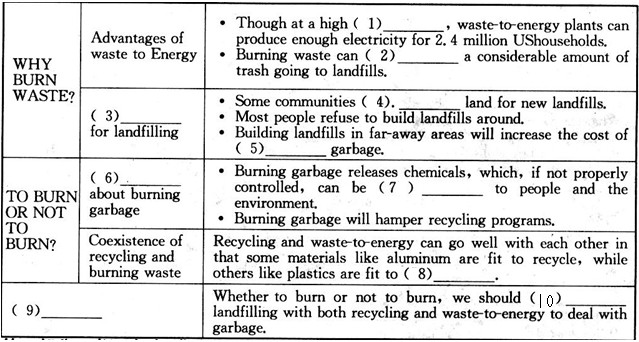
查看习题详情和答案>>WHY BURN WASTE?
Waste-to-energy plants generate (产生) enough electricity to supply 2.4 million households in the US. But,
provrding electricity is not the major advantage of waste-to-energy plants. In fact, it costs more to generate
electrlcity at a waste-to-energy plant than it does at a coal, nuclear, or hydropower plant.
The maior advantage of burning waste is that it considerably reduces the amount of trash going to landfills.
The average American produces more than l,600 pounds of waste a year. If all this waste were landfilled, it
would take more than two cubic yards of landfill space. That's the volume of a box three feet long, three feet
wide, and six feet high. If that waste were burned, the ashes would fit into a box three feet long, three feet
wide, but only nine inches high!
Some communities in the Northeast may be running out of land for new landfills. And, since most people
don't want landfills in their backyards, it has become more difficult to obtain permits to build new landfms.
Taking the country as a whole, the United States has plenty of open space, of course, but it is expensive to
transport garbage a long distance to put it mto a landfill.
TO BURN OR NOT TO BURN?
Some people are concerned that burning garbage may harm the environment. Like coal plants, waste-to-
energy plants produce air pollution when the fuel is bumed to produce steam or electricity. Burning garbage
releases the chemicals and substances found in the waste. Some chemicals can be a threat to people, the
environment, or both, if they are not properly controlled.
Some critics of waste-to-energy plants are afraid that burning waste will hamper (妨碍, 阻碍) recycling
programs. If everyone sends their trash to a waste-to-energy plant, they say, there will be little motive to
recycle. Several states have considered or are cons idering banning waste-to-energy plants unless recycling
programs are in place. Massachusetts, New Jersey, and New York City have delayed new waste-to-energy
plants, hoping to increase the level of recycling first.
So, what's the real story? Can recycling and burning waste coexist? At first glance, recycling and waste-
to-energy seem to be at odds (不一致), but they can actually complement (弥补) each other. That's because
it makes good sense to recycle some materials, and better sense to burn others.
Let's look at aluminum, for example. Aluminum mineral is so expensive to mine that recycling aluminum
more than pays for itself. Burning it produces no energy. So clearly, aluminum is valuable to recycle and not
useful to burn.
Paper, on the other hand, can either be burned or recycled-it all depends on the price the used paper will
bring. Plastics are another matter. Because plastics are made from petroleum and natural gas, they are excellent
sources of energy for waste-to-energy plants. This is especially true since plastics are not as easy to recycle
as steel, aluminum, or paper.
Plastics almost always have to be hand sorted and making a product from recycled plastics may cost more
than making it from new materials.
To burn or not to burn is not really the question. We should use both recycling and waste-to-energy as
alternatives to landfilling.