题目内容
注意:每个空格只填一个单词。
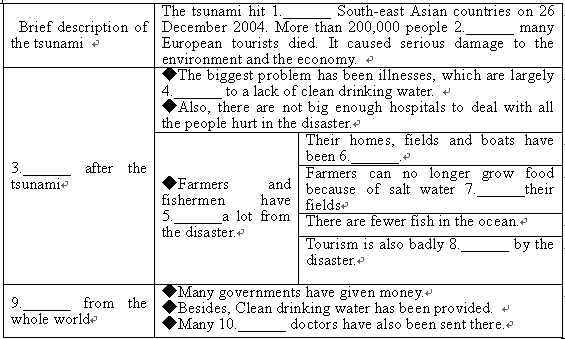
The tsunami (海啸) which hit twelve South-east Asian countries on 26 December 2004 was a great disaster.
More than 200,000 people died in the tsunami. Not only did people living in Thailand, Indonesia and Sri Lanka
die, but many European tourists who were on holiday in these countries also died. Now, we are just beginning
to understand how much damage was caused to the environment and to the economy.
The biggest problem after the tsunami has been illnesses which have spread to many people. These illnesses
are mostly caused by a lack of clean drinking water. People are drinking dirty water because there is no other
water available. This dirty water is making them sick. Also, the hospitals in these poor countries are not big
enough to deal with all the people who were hurt in the tsunami.
Many people who live in the areas hit by the tsunami are farmers and fishermen. The tsunami destroyed
their homes, their fields and their boats. The salt water from the ocean covered the farmers' fields, so they can
no longer grow food. Also, fishermen are finding that there are fewer fish in the ocean. Now, these people,
who were already quite poor, have no way to earn money. No one knows how long it will take for the fish to
return, or for the farmers to be able to grow food again. Tourism is also very important in these areas, but
many famous tourist areas are destroyed during the tsunami.
The whole world is helping these countries recover from the tsunami. Many governments have given aid
money. UNICEF, the United Nations Children's Fund, has set up 200 places where people can get help. It has
also provided clean drinking water. One organization called Médecins Sans Frontières (Doctors without Borders)
has sent many doctors to care for sick people. In Indonesia, some government officials think that some villages
should be moved away from the ocean, and that farmers should learn how to grow different types of food.
No one knows how much money or how much time it will take for this area to recover completely. However,
with the help and aid that is being sent to the affected areas, hopefully it won't take long.
6. detroyed 7. covering 8. affected 9. Aid\Help 10. unknown

 开心蛙状元测试卷系列答案
开心蛙状元测试卷系列答案任务型读写. 请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入恰当的单词。注意:每个空格只填一个单词。(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)
If you are asked to chair a meeting, remember the following six golden rules for meeting management.
1. Always start the meeting on time
If you begin on time, group members who show up late will realize the value of time. Beginning on time reflects the skill as an effective time manager and sets an example for others to follow.
2. Select a note-taker or arrange to have the meeting audio-taped
You may need to refer back to an issue that was discussed during the meeting at a later date. Good record-keeping is a sign of a good meeting manager as well.
3. Learn to listen
So many times we think we are going to say and, in the process, block out important points that other group members may be contributing. Additionally, we often hear only what we want to hear, rather than really listen to other people. Meetings that are characterized by effective listening are successful meetings.
4. Keep the discussion on track
Many times important issues can get sidetracked in a meeting, especially when everyone has a different opinion about the topic. If an unexpected conflict develops once the meeting is in progress, either appoint a subcommittee to look into the problem, or ask the participants involved in the conflict to meet with you after the meeting. Doing so will help keep the discussion on track and minimize (减少) the chances of wasting participants’ time of great value.
5. Give everyone an opportunity to be heard
Some people tend to control meetings, whereas others wait to be asked their opinions. As the leader of the meeting, you need to keep an open mind and make sure everyone feels welcome to contribute and express ideas without criticism.
6. End on time
If you said the meeting would last no longer than one hour, make sure the meeting lasts for only one hour. Running late with a meeting makes members late for other appointments, increases the chances that the members will mentally leave the meeting and reduces your reliability as an effective meeting manager.
Advice on how to 【小题1】 a meeting
| Rules | Reasons |
| Start the meeting on time. | 【小题2】 the skill and set an example. |
| Select a note-taker or 【小题3】 the meeting. | Need to refer to an issue【小题4】 |
| Learn to listen. | Listen【小题5】 to make sure it is a successful meeting. |
| Keep the【小题6】 on track | Minimize the chances of wasting participants’【小题7】 time. |
| Give everyone an 【小题8】 to be heard | Make everyone feel 【小题9】 to speak. |
| End on time. | 【小题10】 your reliability. |
IV: 任务型读写
请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入最恰当的单词。注意:每空格1个单词。
Do American children still learn handwriting in school? In this age of the keyboard, some people seem to think handwriting lessons are on the way out.
Steve Graham, a literacy professor at Vanderbilt University, says he has been hearing about the death of handwriting for the past fifteen years. However, a recent survey shows that it is still being taught by about 90% of teachers in grades one to three. 90% of teachers also say they are required to teach handwriting. But studies have yet to answer the question of how well they are teaching it. Professor Graham says that about three out of every four teachers say they are not prepared to teach handwriting. “And then when you look at how it’s taught, you have some teachers who are teaching handwriting by providing instruction for ten, fifteen minutes a day, and then other teachers who basically teach it for 60 to 70 minutes a day -- which really for handwriting is pretty much death.”
Many adults remember learning by copying letters over and over again. Today’s thinking is that short periods of practice are better. Many experts also think handwriting should not be taught by itself but be used as a way to get students to express ideas. After all, that is why we write.
Handwriting involves two skills. One is legibility (清楚), which means forming the letters so they can be read. The other is fluency -- writing without having to think about it. The professor says fluency continues to develop up until high school.
But not everyone masters these skills. Teachers commonly report about one-fourth of their kids have poor handwriting. Some people might think handwriting is not important anymore because of computers and voice recognition programs. But Professor Graham says word processing is rarely done in elementary school, especially in the early years. Even with high school teachers, we find that less than 50% of assignments are done via word processing or with word processing. And, in fact, if we added in taking notes and doing tests in class, most of the writing done in school is done by hand.
American children traditionally first learn to print, then to write in cursive (草体的), which connects the letters. But actually more than 75% of students choose to print their essay on the test rather than write in cursive.
|
Title |
Write or Wrong: The Death of Handwriting? |
|
Theme |
Handwriting lessons are on the way out. |
|
Present (56)_______ of handwriting lessons |
It’s required to teach by about (57)_____ of teachers in grades one to three; Three out of every four teachers aren’t prepared to teach handwriting; (58) _______ are provided from 10-15 minutes a day to 60-70 minutes a day respectively. |
|
Common (59)________ on teaching handwriting |
Short periods of practice are better; It should not be taught by itself (60)_______ be used as a way to get students to express ideas |
|
Two skills (61)______ in handwriting |
Legibility; (62)_____. |
|
(63)____ of poor handwriting |
Computers and voice recognition programs are (64)________; The fact that most of the writing done in school is done by hand is ignored; More than 75% of students (65)____ printing their essay on tests to writing in cursive. |
任务型读写. 请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入恰当的单词。注意:每个空格只填一个单词。(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)
If you are asked to chair a meeting, remember the following six golden rules for meeting management.
1. Always start the meeting on time
If you begin on time, group members who show up late will realize the value of time. Beginning on time reflects the skill as an effective time manager and sets an example for others to follow.
2. Select a note-taker or arrange to have the meeting audio-taped
You may need to refer back to an issue that was discussed during the meeting at a later date. Good record-keeping is a sign of a good meeting manager as well.
3. Learn to listen
So many times we think we are going to say and, in the process, block out important points that other group members may be contributing. Additionally, we often hear only what we want to hear, rather than really listen to other people. Meetings that are characterized by effective listening are successful meetings.
4. Keep the discussion on track
Many times important issues can get sidetracked in a meeting, especially when everyone has a different opinion about the topic. If an unexpected conflict develops once the meeting is in progress, either appoint a subcommittee to look into the problem, or ask the participants involved in the conflict to meet with you after the meeting. Doing so will help keep the discussion on track and minimize (减少) the chances of wasting participants’ time of great value.
5. Give everyone an opportunity to be heard
Some people tend to control meetings, whereas others wait to be asked their opinions. As the leader of the meeting, you need to keep an open mind and make sure everyone feels welcome to contribute and express ideas without criticism.
6. End on time
If you said the meeting would last no longer than one hour, make sure the meeting lasts for only one hour. Running late with a meeting makes members late for other appointments, increases the chances that the members will mentally leave the meeting and reduces your reliability as an effective meeting manager.
Advice on how to 1. a meeting
|
Rules |
Reasons |
|
Start the meeting on time. |
2. the skill and set an example. |
|
Select a note-taker or 3. the meeting. |
Need to refer to an issue4. |
|
Learn to listen. |
Listen5. to make sure it is a successful meeting. |
|
Keep the6. on track |
Minimize the chances of wasting participants’ 7. time. |
|
Give everyone an 8. to be heard |
Make everyone feel 9. to speak. |
|
End on time. |
10. your reliability. |
| 任务型读写 请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入最恰当的单词. 注意:每个空格只填1 个单词. When we think of leadership, we often think of strength and power. But what are these really and how do they operate? Leadership today is not about forcing others to do things. Even if this is possible, it is shortterm, and tends to backfire( 产生事与愿违的后果). If you order someone to do something against their will, they may do it because they feel they must, but the anger they feel will do more harm in the longterm. They will also experience fear. Fear causes the thinking brain to shut down, making the person unable to function at his or her best. If they associate you with this emotion of fear, they will become less functional around you, and you will have succeeded in not only shooting yourself in the foot, but possibly making a very good employee or partner unable to perform effectively. Fear has no place in leadership. The way we influence people in a lasting way is by our own character, and our understanding and use of emotion. We can order someone to do something, which may be part of the work day or we can employ them at the emotional level, so they became fully devoted to the projects and provide some of their own motivations. Today's work place is all about relationships. Anyone works harder in a positive environment in which they're recognized and valued as a human being as well as a worker. Everyone produces just a bit more for someone they like. Leaders understand the way things work. They know the paycheck is not the single most motivating factor in the work life of most people. The true strength of leadership is an inner strength that comes from the confidence of emotional intelligence-knowing your own emotions, and how to handle them, and those of others. Developing your emotional intelligence is the single best thing you can do if you want to develop your relationships with people around you, which is the key to the leadership skills.
|
IV. 任务型读写
请认真阅读下面短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填上最恰当的单词。注意:每空格1个单词。
The ups and downs of life may seem to have no predictable plan. But scientists know there are very definite patterns that almost all people share. Even if you’ve passed some of your “prime”, you still have other prime years to experience in the future. Certain important primes seem to peak later in life. It is really good news to many of us who don’t have a good feeling about ourselves now. We needn’t be worried about it now. When are you smartest? From 18-25, according to IQ scores; but you’re wiser and more experienced with increasing age.
You’re sharpest in your 20’s; around 30, memory begins to decline. But your IQ for other tasks climbs. Your vocabulary at the age of 45, for example, is three times as great as when you graduated from college. At the age of 60, your brain possesses almost four times as much information as it did at the age of 21. It is really amazing, but it is true.
When are you happiest? You have the best physical sense of yourself from 15 to 24; the best professional sense from 40 to 49.
Before age 24, we believe that our happiest years are yet to come; over 30, we believe that they’re behind us.
When are you most creative? Generally between 30 and 39, but the peak varies with different professions.
Mozart wrote a symphony and four sonatas by age eight, and Mendelssohn composed his best known work A Midsummer Night’s Dream, at 17, but most of the great music was written by men between 33 and 39.
Though the peak in most fields comes early-most Nobel prizewinners did their top research in their late 20’s and 30’s — creative people continue to produce quality work throughout their lives. For the “well-conditional mind”, there is no upper limit.
So if you are not very successful at present, it really doesn’t matter. Just have a little patience and wait for your best time.
| Title: Best time in life | |
| The smartest age | We have the (56) IQ between the (57) of 18 and 25. |
| The sharpest age | We are sharpest in our 20’s. |
| We have the (58) vocabulary at the age of 45. | |
| We possess the largest (59) of information at the age of 60. | |
| The happiest age | We are happiest at a time (60) the age of twenty and (61) the age of 30. |
| The most creative age | Most of us have the greatest (62) ability between the ages of 30 and 39. |
| Most people (63) their Nobel Prizes in their late 20’s and 30’s. | |
| People with well-conditioned (64) ________ are creative (65) their lives. | |