题目内容
Sam remembered several occasions in the past ______ he had experienced a similar feeling.
A. what B. which C. where D. why
C

People do not analyze every problem they meet. Sometimes they try to remember a solution from the last time they had a 21 problem. They often accept the opinion or ideas of other people. Other times they begin to act without 22 ;they try to find a solution by trial and error. 23 .,when all of these methods 24 ,the person with a problem has to start analyzing. There are six 25 in analyzing a problem.
26 the person must recognize that there is a problem. For example, Sam's bicycle is broken, and he cannot ride it to class as he usually does. Sam must see that there is a problem with his bicycle.
Next the person must 27 the problem. Before Sam can repair his bicycle, he must know why it does not work. For example, he must determine the parts that are wrong.
Now the person must look for 28 that will make the problem clearer and lead to possible solutions. For example, suppose Sam 29 that his bike does not work because there is some thing wrong with the brakes(刹车). 30 , he can look in his bicycle repair book and read about brakes, 31 his friends at the bike shop, or look at his brakes carefully.
After studying the problem, the person should have 32 suggestions for a possible solution. Take Sam as an example 33 ,his suggestions might be: tighten or loosen the brakes; buy new brakes and change the old ones.
In the end, one 34 seems to be the solution to the problem. Sometimes the __35__ idea comes quite 36 because the thinker suddenly sees something new or sees something in a 37 way. Sam, for example, suddenly sees there is a piece of chewing gum(口香糖)stuck to a brake. He 38 finds the solution to his problem :he must___39___the brake.
Finally the solution is tested .Sam finds that his bicycle 40 perfectly. In short he has solved the problem.
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
|
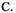 . similar D. common
. similar D. common rich information. A search engine with fast speed and various resources will be of great help to him. Which web will he refer to?
rich information. A search engine with fast speed and various resources will be of great help to him. Which web will he refer to? similar D.
common
similar D.
common