题目内容
The Sun is the major source of energy for our planet. It causes the evaporation (蒸发) of water from the
oceans and lakes. Sunlight also provides the energy used by green plants to make their own food. These
green plants then provide food for all organisms (生物) on the Earth.
Much of the energy that comes from the Sun never reaches the Earth's surface. It is either reflected
or absorbed by the gases in the upper atmosphere. Of the energy that reaches the lower atmosphere, 30%
is reflected by clouds or the Earth's surface. The remaining 70% warms the surface of the planet, causes
water to evaporate, and provides energy for the water cycle and weather. Only a tiny part, approximately
0.023%, is actually used by green plants to produce food.
Many gases found in the atmosphere actually reflect heat energy escaping from the Earth's surface back
to the Earth. These gases act like the glass of a greenhouse in that they allow energy from the Sun to enter
but prevent energy from leaving. They are therefore called greenhouse gases.
When sunlight strikes an object, some of the energy is absorbed and some is reflected. The amount
reflected depends on the surface. For example, you've probably noticed how bright snow is when sunlight
falls on it. Snow reflects most of the energy from the Sun, so it contributes to the low temperatures of winter.
Dark-coloured surfaces, such as dark soil or forest, absorb more energy and help warm the surrounding air.
B. water from oceans and lakes
C. energy from the Sun
D. greenhouse gases in the sky
B. reflected by the gases in the upper atmosphere
C. lost in the upper and lower atmosphere
D. used to evaporate water from the oceans and lakes
B. a forest looks dark in winter because it absorbs solar energy
C. only 0.023% of the energy from the Sun is made use of on the Earth
D. greenhouse gases allow heat energy to escape from the Earth's surface

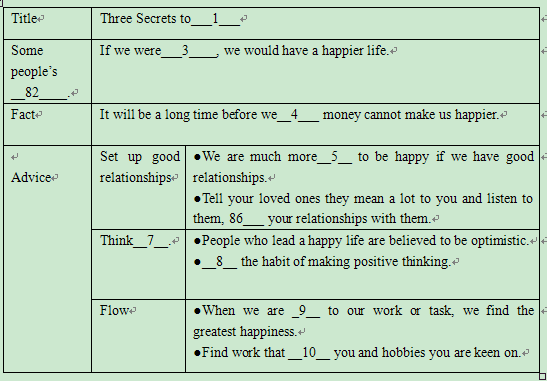
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 e things before we realize that. So what will bring
e things before we realize that. So what will bring