题目内容
B. much popular
C. more popular
D. the most popular

Tony Buzan’s grades were going down at university. Disappointed with his low marks, he went to the library to find a book on how to use his brain. He was directed to the medical section. Confused, he said to the librarian, “I don’t want to take my brain out, I just want to learn how to use it.” Her reply was simple: “There’s no book on that.”
“I thought to myself,” says Buzan, “if I buy a little radio, I get an instruction manual (说明书). If I buy a microwave, I get an instruction manual. But for the most important machine in the world, no instruction manual?”
Fifty years later, Buzan has become the world’s leading speaker on the brain and learning. In the late 1960s, he invented the mind map, a visual representation of thought processes.
This kind of thinking has become a popular tool for planning, organizing, problem solving, and communicating across the world. He has since authored and co-authored over 100 books that have appeared in more than 30 languages.
“I think in most cases, people use less than 1 percent of their brains,” he says.
But how do you expand this 1 percent? How do you become the best student you can be?
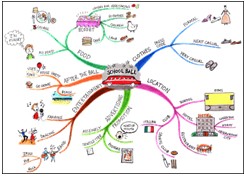
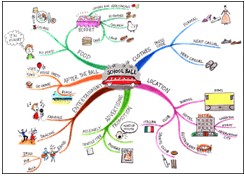
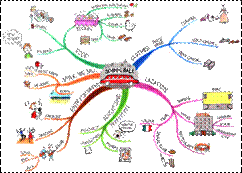
According to Buzan, the answer is simple. You take a section of whatever it is that you are trying to learn, he says, and you read it for its essence (精髓、要素). Then you make a mind map of all the important details. For a truly effective mind map, you start with a colored image in the center of your page. Draw the first image that comes to mind on the topic you are mind mapping. Branch off from your central image and create one of your main ideas. From your main branches draw some sub-branches and from those sub-branches you can draw even more branches. He emphasizes that you should use plenty of images and colors as these help with memory recall and encourage creativity.
By using this visual format (形式), according to Buzan, your mind will begin to make associations that will help you remember more information for longer periods of time.
Buzan believes that traditional note-taking methods, such as lists and summaries, do not stimulate the brain’s recall capacity or ability in the same way. Because of this, students will often find themselves locked away in their rooms for hours, trying hard to memorize separate details. Buzan believes that for a more effective and lasting way of studying, you must first understand how your brain works.
“Everyone is born smart,” he says. “You just have to learn how to learn.”
【小题1】What is the main purpose of the first two paragraphs?
| A.To show that Tony Buzan was worried about his study. |
| B.To invite us to think about the importance of manuals. |
| C.To prove that the mind map is a useful tool for the brain. |
| D.To show why Tony Buzan studies the brain and learning. |
| A.Excite. | B.Improve. | C.Encourage. | D.Affect. |
| A.If we learn the mind map, we will become the best student. |
| B.The mind map will help your brain connect separate details. |
| C.The mind map will be more effective if we put more details in it. |
| D.We will solve the problem if we make connections between ideas. |
| A.How to make the mind map? |
| B.Is the mind map widely used? |
| C.Can your memory be mapped? |
| D.Is the mind map helpful in thinking? |
In life, people come across many experiences, which they remember all their lives. I had a similar experience, too.
It was the day of my last paper of the final exam. My uncle had invited me to spend my vacation with him. I was especially excited about the invitation that my uncle had given me to stay with him for a few days in Cambridge.
On that day we got into our classroom. The teacher quickly handed out the paper. The exam would last two hours and some of the expected questions came. I finished it almost forty-five minutes earlier. But since it was a rule not to collect the paper before the allotted(规定的)time. I had to sit till the teacher collected the paper. I checked my paper twice and corrected some of the mistakes in it. I started thinking about the place my friends and I had planned to go to after the exam. The time seemed to be endless. So I thought of drawing something on the paper and turned it overleaf. I was shocked to see that the page which I had supposed to be blank had four more questions on it which carried 20 marks and would take at least half an hour to complete. There were only 10 minutes left. I was so nervous that I could hardly write anything. They were the sub-questions(小题)of the last question. Suddenly our physics teacher came in and told all of us that in the last question, out of 6 sub-questions only 2 had to be solved. I felt very relieved.
From then on, I realized that my anxiousness and excitement could have cost me to lose 20 marks and decided never to make such a mistake again.
【小题1】Which of the following statements is true?
| A.The writer didn’t work hard at physics. |
| B.The writer lost 20 marks for the last question. |
| C.The writer made some mistakes during the exam. |
| D.The questions on the paper were difficult for the writer. |
| A.less worried | B.less afraid |
| C.more surprised | D.more nervous |
| A.the writer did 2 sub-questions of the last question |
| B.the writer finished doing all the sub-questions |
| C.the writer spent 45 minutes finishing the paper |
| D.the writer got full marks in the physics exam |
| A.learn some exam skills |
| B.be careful not to make mistakes in the exam |
| C.try our best to do well in the exam |
| D.concentrate on what we are doing |
 Tony Buzan’s grades were going down at university. Disappointed with his low marks, he went to the library to find a book on how to use his brain. He was directed to the medical section. Confused, he said to the librarian, “I don’t want to take my brain out, I just want to learn how to use it.” Her reply was simple: “There’s no book on that.”
Tony Buzan’s grades were going down at university. Disappointed with his low marks, he went to the library to find a book on how to use his brain. He was directed to the medical section. Confused, he said to the librarian, “I don’t want to take my brain out, I just want to learn how to use it.” Her reply was simple: “There’s no book on that.”